Adobe xd dmg. Read Book Juvenile Delinquency Causes And Controljuvenile delinquency is a teen’s regular exposure to violence. This is one of the major causes of juvenile crime, particularly violent juvenile crime. Exposure to violence takes many forms: abuse at the hands of a parent or another household member, or witnessing domestic violence between. Juvenile delinquency: causes and control: Agnew, Robert. An essential resource for exploring juvenile delinquency in the twenty-first century, Juvenile Delinquency: Causes and Control, Fourth Edition, offers a clear and concise overview of the latest theories and research on the causes and control of delinquency.



Timothy Brezina is the author of 'Juvenile Delinquency: Causes and Control', published 2011 under ISBN 142 and ISBN. St cleaner license key free. read more Marketplace prices. Agnew, Robert is the author of 'Juvenile Delinquency: Causes and Control', published 2014 under ISBN 462 and ISBN. read more Marketplace prices. Check genuine yonex serial number. Bomberman game.
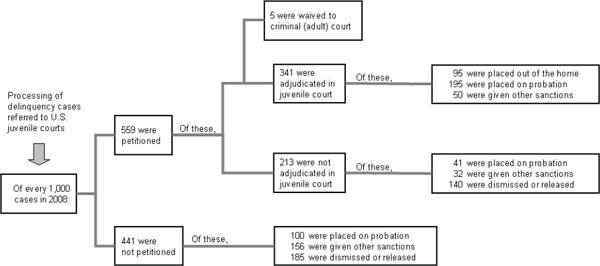
What Is Juvenile Delinquency
Table of Contents
Juvenile Delinquency Causes And Control 4th Edition 2017

Juvenile Delinquency Causes And Control 4th Edition 10th
- Each chapter end with Test Your Knowledge of this Chapter, Thought and Discussion Questions, Key Terms, and Endnotes sections.
PART 1. THE NATURE AND EXTENT OF DELINQUENCY
1. What Is Delinquency and How Does It Differ from Adult Crime
Juvenile Delinquents Are Viewed Differently than Adult Criminals
Juvenile Delinquents Are Treated Differently than Adult Criminals
Special Laws for Juveniles: Status Offenses
A Special Court for Juveniles: Juvenile Court
Special Correctional Programs for Juveniles
How Can We Explain the Invention of Juvenile Delinquency?
Changing Conception of Children
Major Social Changes, Especially the Growth of Urban Slums
Gender, Race, and the Invention of Delinquency
Our View and Treatment ofJuvenile Offenders Continues to Evolve
'Getting Tough' with Juvenile Offenders (Late 1980s through the Early 2000s)
Retreating from the Get-Tough Approach (Since the Early 2000s)
Summary
Teaching Aids
Web-Based Exercises
Controversial Case
2. How Is Delinquency Measured?
Official Statistics--Especially Arrest Data from the Police
Problems with Arrest Data
Summary
Self-Report Data
How Do We Know that Juveniles Are Telling the Truth?
Problems with Many Self-Report Surveys
Recent Self-Report Surveys Have Made Much Progress in Overcoming the Preceding Problems
Victimization Data
Problems with Victimization Data
Summary
Teaching Aids
A Challenge
Practical Advice: Three Things to Beware of WhenOthers Discuss the Extent of and Trends in Delinquency (and a Challenge)
Web-Based Exercise: Measuring the Extent of Rape
Answers to the Challenge
3. How Much Delinquency Is There, and Is Delinquency Increasing?
How Much Delinquency Is There?
How Many Juveniles Are Arrested, and What Are They Arrested For?
How Much Self-Reported Delinquency Is There?
How Many Juveniles Are Victimized, and How Many Victimizations Are Committed by Juveniles?
Summary
Is Juvenile Delinquency Increasing?
Are Juvenile Arrests Increasing?
Is Self-Reported Delinquency Increasing?
Are Victimizations Committed by Juveniles Increasing?
Summary
How Can We Explain the Dramatic Decline in Serious Crime Since the Mid-1990s?
Teaching Aids
Exercise: The Extent of and Trends in Campus Crime
Web-Based Exercise: Finding the Latest Information on the Extent of and Trends in Crime and Delinquency
4. Who Is Most Likely to Engage in Delinquency?
Is Social Class Related to Delinquency?
Early Studies Based on Arrest Data
Early Self-Report Studies
Criticisms of the Early Self-Report Studies
The Later Self-Report Studies
Summary
Are Race and Ethnicity Related to Delinquency?
Arrest Data
Criticisms of Arrest Data
Self-Report Data
Victimization Data
Is Race Related to Delinquency?
Are Race Differences in Serious Delinquency Explained by Social Class?
Is Age Related to Delinquency?
Is Gender Related to Delinquency?
Arrest Data
Self-ReportData
Summary
Are There Different Types of Delinquents?
An Overview of the Research on the Different Types of Delinquents
What Are the Different Types of Delinquents?
Summary
Teaching Aids
Exercise 1: Perceptions of Race and Crime
Exercise 2: Why Do Asian Americans Have Lower Crime Rates?
Exercise 3: Explaining the Association Between Gender and Crime
Exercise 4: Girls' Delinquency
PART 2. THE CAUSES OF DELINQUENCY: THEORIES
5. What Is a Theory and How Do We Test Theories?
What Is a Theory?
What Are the Basic Parts of a Theory?
Why Is It Important to Study Theories of Delinquency?
How Do We Test Theories of Delinquency (or Determine Whether Some Factor Causes Delinquency)?
The Scientific Method
Carefully Define Your Independent and Dependent Variables
Decide How to Gather Data to Test Your Belief or Theory
Develop Measures of Your Independent and Dependent Variables
Select a Sample of Juveniles to Survey
Analyze the Data You Have Collected
Summary
Teaching Aids
Some Challenges
Web-Based Resources for Your Criminological Research Project
Answers to the Challenges
6. Strain Theory
What Are the Major Types of Strain?
The Failure to Achieve Your Goals
Loss of Positive Stimuli/Presentation of Negative Stimuli
What Impact Does Strain Have on the Juvenile?
Why Are Some Juveniles More Likely to Cope with Strain Through Delinquency?
Summary
Teaching Aids
Case Studies
Web-Based Exercise:Applying Strain Theory
7. Social Learning Theory
Juveniles Learn to Engage in Delinquency from Others
The Differential Reinforcement of Delinquency
The Frequency, Amount, and Relative Probability of Reinforcement
Positive and Negative Reinforcement
Punishment
The Sources of Reinforcement and Punishment
Some Individuals Are More Likely to Be Reinforced for Delinquency than Others
Intermittent Reinforcement
Discriminative Stimuli
Research on the Reinforcement and Punishment of Delinquency
Beliefs Favorable to Delinquency
Generally Approve of Minor Delinquency
Conditionally Approve of Delinquency, Including Some Serious Delinquency
General Values Conducive to Delinquency
Where Do the Beliefs Favorable toDelinquency Come From?
The Imitation of Delinquent Models
Summary
Teaching Aids
Controversial Cases
Web-Based Exercise: Learning to Hate
8. Control Theory
Why Do Juveniles Conform (and Sometimes Deviate)?
How Is Control Theory Similar to and Different from Social Learning Theory?
What Are the Major Types of Control (or Restraints to Delinquency)?
Direct Control
Stake in Conformity
Belief
Self-Control
Summary
Teaching Aids
Controversial Issue: The Nature of Human Nature
Controversial Methods for Increasing Direct Control
Web-Based Exercise: Where Do Theories Come From?
9. Labeling Theory
Background on Labeling Theory
How Do Others React to the Juvenile's Delinquency?
Harsh/Rejecting Reaction
Failure to Respond to the Juvenile's Delinquency
'Condemn the Delinquency but Accept the Juvenile' Reaction
Summary
Why Does the Harsh/Rejecting Reaction Lead to Further Delinquency?
Reduces Control
Increases Strain
Increases the Social Learning of Delinquency
Creates a Delinquent Self-Concept
What Determines Whether Juveniles Experience the Harsh/Rejecting Reaction?
Are Some Juveniles More Likely than Others to Respond to the Harsh/Rejecting Reaction with Further Delinquency?
The Evidence on Labeling Theory
Summary
Teaching Aids
Controversial Issue #1: Going Too Far? Zero-Tolerance Policies in the Nation's Schools
Controversial Issue #2: Is It Sometimes Best to Ignore Delinquency?
Web-Based Exercise: Applying Labeling Theory (Race and Labeling)
10. The Life Course
Why Do Most Individuals Increase Their Levels of Offending During Adolescence?
The Biological and Social Changes Associated with Adolescence
A Reduction in Control
An Increase in the Social Learning for Crime
An Increase in Strain
Summary
Why Do a Small Percentage of Individuals Offend at High Rates over Much of Their Lives?
Traits Conducive to Crime
Poor Parenting
High Rates of Offending over the Life Course
Summary
Summary
Teaching Aids
Web-Based Exercise: Comparing Adult and Juvenile Offenders
Controversial Issue: An Evolutionary Theory of Adolescence-Limited Offending
11. Is Delinquency More Likely in Certain Typesof Situations?
What Types of Situations Are Most Conducive to Delinquency?
Strain Theory: Situational Strains
Strain Theory: Situational Factors that Increase the Likelihood of Delinquent Coping
Social Learning and Control Theories: The Benefits and Costs of Delinquency
Attractive Targets
The Absence of Capable Guardians
The Presence of Delinquent Peers
Summary
What Factors Influence the Likelihood that Predisposed Offenders Will Encounter Situations Conducive to Delinquency?
The Nature of the Individual's Routine Activities
Factors Influencing Routine Activities
Summary
Summary
Teaching Aids
Applying the Research: Examining the Routine Activities of College Students
Web-Based Exercise: Crime PreventionThrough Environmental Design
12. Group Differences in Delinquency
Why Are Crime Rates Higher in Some Communities than in Others?
What Are the Characteristics of High-Crime Neighborhoods and Cities?
Summary
Are Communities with Characteristics Conducive to Crime Becoming More Common?
Why Are Deprived Communities Higher in Crime?
Deprived Communities Are Higher in Strain
Deprived Communities Are Lower in Control
Deprived Communities Foster the Social Learning of Crime
Community Crime Rates Reduce Control, Foster the Social Learning of Crime, and Increase Strain
Overview of the Leading Theories of Delinquency
Teaching Aids
Exercise: Increasing Community Control
Exercise: Explaining Other Group Differences in Crime
Web-Based Exercise: Societal Differences in Crime and Delinquency
PART 3. THE CAUSES OF DELINQUENCY: RESEARCH
13. Individual Traits
Are Juveniles with Certain Traits More Likely to Engage in Delinquency?
Low Verbal IQ
Low Self-Control
Irritability
Summary
Why Are Some Individuals More Likely than Others to Possess These Traits?
Biological Influences on Traits
Environmental Influences on Traits
Is Mental Illness Related to Violence?
Summary
Teaching Aids
Controversial Issue: Should Delinquents Be Held Responsible for Their Behavior?
Web-Based Exercise: Programs for Mentally Ill Offenders
14. The Family
The Effect of the Family on Delinquency
Family Structure
Are Juveniles from Single-ParentHomes More Delinquent?
Does the Mother's Employment Outside the Home Increase Delinquency?
Does Placing Juveniles in Childcare Facilities Increase the Likelihood of Delinquency?
Are Teenage Parents More Likely to Have Delinquent Children?
Are Juveniles from Large Families More Delinquent?
Parental and Sibling Crime/Deviance
Are Juveniles with Criminal or Deviant Parents and Siblings More Likely to Be Delinquent?
The Quality of Family Relationships
Are Juveniles Who Have Warm or Close Relationships with Their Parents Less Delinquent?
Parental Socialization
What Should Parents Do to Teach Their Children to Avoid Delinquency?
What Should Parents Do to Teach Their Children to Engage in Conventional Behavior?
Summary
Why Do SomeParents Employ Poor Parenting Practices?
A Note on Genes, Parenting, and Delinquency
Teaching Aids
Exercise: Putting Your Knowledge to Use
Web-Based Exercise: An Inside Look at a Troubled Family
15. The School
What School Experiences Contribute to Delinquency?
Do School Experiences Cause Delinquency?
Why Do Some Juveniles Have Negative School Experiences?
School Characteristics and Delinquency
How Much Delinquency Occurs at School?
How Can We Explain School Differences in Delinquency?
Teaching Aids
Applying Theories and Research
Web-Based Exercise: More Information on School Violence, Including Bullying
16. Delinquent Peers and Gangs
What Impact Do Delinquent Peers Have on Delinquency?
Under WhatConditions Are Delinquent Peers Most Likely to Cause Delinquency?
What Are Delinquent Peer Groups Like?
Why Are Individuals in Delinquent Groups More Likely to Engage in Delinquency?
Why Are Some Juveniles More Likely than Others to Get Involved with Delinquent Peers?
What Impact Do Gangs Have on Delinquency?
What Is a Street Gang?
How Common Are Gangs?
Are Gangs Becoming More Common?
What Effect Do Gangs Have on Crime and Delinquency?
What Are the Characteristics of Gang Members?
How Are Gangs Organized or Structured?
What Are Female Gangs Like?
Why Do Some Juveniles Join Gangs?
Why Do Some Communities Develop Gangs?
How Can We Explain Long-Term Trends in Gang Activity?
Summary
Teaching Aids
ControversialIssue: What Is a Gang?
Web-Based Exercise: An Examination of Two Major Gangs
17. Other Social Influences
Does Religion Reduce Delinquency?
The Evidence
Does Work Reduce Delinquency Among Juveniles Attending School?
The Evidence
Does Mass Media Violence Cause Violence Among Juveniles?
TV and Movie Violence
Violent Video Games
Music with Violent Themes
Does Media Violence Affect Some Juveniles More than Others?
Summary
Does Social Media Engagement Increase the Risk of Delinquent Behavior?
The Evidence
Summary
Do Drugs Increase the Likelihood of Delinquency?
Reasons that Drugs May Affect Delinquency
The Evidence
Do Guns Increase the Likelihood of Delinquency?
How Common Is Gun Ownership andPossession Among Juveniles?
Do Guns Contribute to Delinquency?
Do Guns Prevent More Crime than They Contribute To?
Summary
Teaching Aids
Controversial Issue: Should Marijuana Be Legalized?
Web-Based Exercise: Guns Across the Globe
18. Pulling It All Together
A Brief Review of the Theories and Research on the Causes of Delinquency
Theories
Research
A General Theory of Delinquency
The Major Direct Causes of Delinquency and Why They Cause It
How All These Clusters Are Related
How Biological Factors and the Larger Social Environment Affect the Clusters
Explaining Group Differences In Delinquency
Using the General Theory to Explain Why Males Have Higher Rates of Delinquency than Females
The Special Role ofSexual Abuse in Explaining Serious Female Offending
An Overview of the General Theory of Delinquency
Teaching Aids
Web-Based Exercise: Applying the General Theory
PART 4. THE CONTROL AND PREVENTION OF DELINQUENCY
19. Policies and Programs
The Experimental Model for Determining Program Effectiveness
The Importance of Doing Randomized Experiments
Problems in Doing Randomized Experiments
What If One Is Not Able to Do a Randomized Experiment?
Why Are Some Programs Ineffective at Reducing Delinquency?
Summary
Teaching Aids
Web-Based Exercise: The Importance (and Sometimes Neglect) of Good Evaluation Research
Some Challenges
Answers to Challenges
20. The Police
How Do the Police Operate?
PreventivePatrol Is the Major Type of Policing
The Police Spend Only a Small Amount of Their Time Dealing with Crime
Policing Is Primarily Reactive in Nature
When the Police Do Discover or Hear About a Crime, They Usually Do Not Catch the Offender
If the Police Do Catch a Suspect, They Usually Do Not Arrest the Person
How Effective Is Preventive Patrol?
How Can the Police Increase Their Effectiveness?
Will Hiring More Police Reduce Delinquency?
Will Police Crackdowns Reduce Delinquency?
Will Community Policing Reduce Delinquency?
Summary
Teaching Aids
Web-Based Exercises
21. Juvenile Court and Corrections
What Happens When Juveniles Are Sent to Juvenile Court?
What Are the Major Goals of Juvenile Court?
How Many CasesDoes Juvenile Court Handle, and What Types Does the Court Deal With?
What Are the Major Stages in the Juvenile Court Process?
Juvenile Corrections: What Happens to Juveniles Who Receive a Disposition or Sentence from the Court?
Formal Probation
Intermediate Sanctions
A Renewed Focus on Rehabilitation
Out-of-Home Placements
Aftercare Services
An Overview of the Juvenile Justice Process
Teaching Aids
Controversial Issue
Web-Based Resources and Activities
22. The Juvenile Justice System
Does the Juvenile Justice System Discriminate Against African Americans?
The Extent of Discrimination Varies Across Police Departments and Juvenile Courts
The Extent of Discrimination May Vary by Type of Crime
Small Amounts ofDiscrimination at Different Points in the Juvenile Justice Process Can Have a Large Overall Effect
Racial Discrimination May Be Direct or Indirect
What Can Be Done to Address the Overrepresentation of Minorities in the Juvenile Justice System?
Does the Juvenile Justice System Discriminate Against the Poor and Against Males or Females?
Summary
Teaching Aids
Controversial Issue
Race and Experiences with the Police
Web-Based Exercise: The Disproportionate Minority Contact Initiative
23. The Strategies of Deterrence and Incapacitation
Are the Juvenile Court and Correctional System Tough Enough in Dealing with Offenders, Especially Serious
Offenders?
Efforts to Get Tough with Serious Offenders
Some Get-Tough Measures
HowEffective Are Get-Tough Measures, and What Can Be Done to Increase Their Effectiveness?
Deterrence
Specific Deterrence
General Deterrence
Incapacitation: Will Locking Up Delinquents Reduce Delinquency?
Summary
Teaching Aids
Controversial Issue: Life Without Parole for Juvenile Offenders?
Web-Based Exercise: Restorative Justice in Practice
24. The Strategies of Prevention and Rehabilitation
A Brief History of Prevention and Rehabilitation
How Effective Are Prevention and Rehabilitation Programs?
General Characteristics of Effective Prevention and Rehabilitation Programs
What Are the Characteristics of Successful Prevention/Rehabilitation Programs in Different Areas?
Programs Focusing on the Early Family Environment
Parent Training Programs
Programs Focusing on School Factors
Programs Focusing on Individual Traits
Programs Focusing on Delinquent Peers and Gangs
Selected Other Prevention and Rehabilitation Programs
The Critical Role of Larger Social Forces in Preventing Delinquency
Summary
Teaching Aids
Web-Based Exercise: Finding the Latest Information on Programs and Practices for Reducing Delinquency
Exercise: Extend Your Knowledge of Rehabilitation and Prevention Programs
25. What Should We Do to Reduce Delinquency?
We Should Place More Emphasis on Prevention and Rehabilitation
We Should Hold Juveniles Accountable for Their Behavior and Protect the Community
Teaching Aids
Exercise: What Should We Do to Reduce Delinquency?
Web-Based Exercise: Interested in a Career in Criminology/Corrections?
References
Photo Credits
Author Index
Subject Index